nCode DesignLife破解版是功能强大的基于CAE的疲劳分析软件,使用旨在简化CAE耐久性流程,使用FEA结果进行疲劳分析拥有先进的疲劳寿命预测技术,并通过计算机辅助工程(CAE)的压力进行疲劳分析。软件能够有效减少对物理测试的依赖,避免进行昂贵的设计和工具更改。并提供更快更智能的物理测试,可提供超多的设计选项,从而有效降低相关资源成本,此外,软件还提供完整的质量分析过程和详细的报告,软件以最大限度减少故障和保修的需求,nCode DesignLife是一种前端设计工具,可识别关键位置并根据金属和复合材料的领先有限元(FE)结果计算实际疲劳寿命。 用户不仅可以执行简化的应力分析,还可以通过模拟实际的加载条件来避免过度设计产品,从而避免进行昂贵的设计更改。DesignLife具有用于虚拟振动筛测试,焊接,振动,裂纹扩展,复合材料和热机械疲劳分析的高级功能。本次带来最新2020破解版下载,有需要的朋友不要错过了!
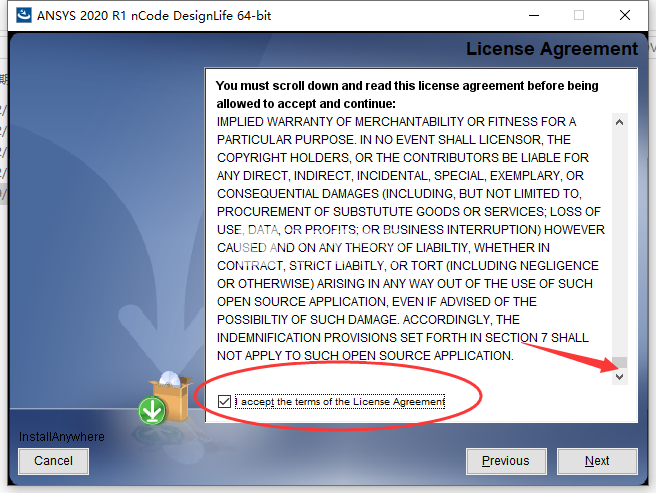
1、在本站下载并解压,加载Ansys.NCODE.2020R1.Win64.iso,双击setup.exe运行安装,如图所示,将滑块滑到底,然后勾选接受许可协议选项
DesignLife翻译现在支持对称模型 – 添加了两个新属性; SymmetryType(Normal或Axisymmetry)和Normal symmetry SymmetryDefinitionFilename。对称定义文件具有节点集,用于定义实体元素的对称面和/或壳单元的对称边
现在,NodeOnElement,AverageNodeOnElement,CriticalDistance和Element解决方案位置支持平面应力和平面应变元素。它们可以与Symmetry一起使用。
振动CAE疲劳字形中振动载荷提供者的CycleCountBins属性的默认值已更改为128.在2018年版本中,此值从64增加到2048,虽然这会使准确度略有提高,但使用128的结果被认为是足够的准确,分析会更快。
软件优势
1、 主要特征
用于多轴,焊接,短纤维复合材料,振动,裂纹扩展,热机械疲劳的先进技术...
直观的图形界面,可根据领先的FEA结果数据进行疲劳分析,包括ANSYS,Nastran,Abaqus,Altair OptiStruct,LS-Dyna等
多线程和分布式处理能力,用于处理大型有限元模型和完整的使用时间表
将CAE与物理测试数据直接关联的单一环境
2、 好处
减少对物理测试的依赖,避免昂贵的设计和工装变更
通过先模拟来执行更智能,更快的物理测试
通过减少故障来减少保修要求
通过评估更多设计方案来降低成本和重量
通过标准化的分析流程提高一致性和质量
高度可配置的专业用户
功能特色
1、用于高级疲劳分析的核心功能
疲劳和耐用性分析可为实际使用环境中的产品使用寿命提供有价值的预测。
通过直接从有限元模型预测结构性能,nCode DesignLife提供了在设计周期早期进行疲劳设计的机会,从而最大程度地减少了原型测试和设计成本。
2、虚拟应变计和虚拟传感器
启用测试结果与有限元结果之间的关联。 可以将量规(单个或玫瑰花结)或位移传感器图形化并定位在有限模型上,作为后处理步骤。 可以提取由于施加载荷而产生的时间历史,以便与测得的应变数据和位移数据直接相关。
3、裂纹增长
使用行业标准方法为FE模型上的指定位置提供完整的断裂力学能力。 内置的增长法律包括NASGRO,Forman,Paris,Walker等。
从提供的几何库中选择或提供自定义应力强度因子。
4、FE显示器
启用带有应力结果轮廓的有限元模型的图形显示。 有限元结果或动画文件中的动画位移显示了载荷下的结构变形。
5、应力寿命分析
在标称应力控制疲劳寿命的高循环疲劳下实现疲劳寿命生产。
包括根据温度在材料曲线之间插值的功能
6、定制分析
使Python或MATLAB脚本可用于扩展现有的分析功能-完美适用于专有方法或研究项目。
7、信号处理
包含nCode基础知识,用于基本数据操作,分析和可视化。 可以通过选择并构建多个案例来定义占空比。 此功能使创建重复的复合占空比变得很容易。
8、材料经理
可以添加,编辑和绘制材料数据。
包含具有许多常用材料疲劳特性的标准数据库。
9、振动管理器
允许输入,编辑和查看振动规范数据。 包含一个具有100多个振动条目的标准数据库。
使用说明
DesignLife选项一、DesignLife选项
1、压力寿命(SN)
应力寿命方法的主要应用是高周疲劳(长寿命),其中名义应力控制疲劳寿命。 提供了多种方法来定义SN曲线,包括针对多个因素(例如平均应力或温度)内插多个材料数据曲线的能力。 还提供其他选项来考虑应力梯度和表面光洁度。 为了获得最大的灵活性,Python脚本启用了自定义疲劳方法和材料模型的定义。
2、应变寿命(EN)
应变寿命方法适用于广泛的问题,包括低周疲劳,其中局部弹塑性应变控制疲劳寿命。
标准的EN方法使用Coffin-Manson-Basquin公式,定义了应变振幅ea与失效循环次数N'之间的关系。 材质模型也可以使用常规查找曲线来定义。 这样就可以插入多个材料数据曲线,以求出平均应力或温度等因素。
3、点焊
点焊选项可以对薄板中的点焊进行疲劳分析。该方法基于LBF方法(请参见SAE论文950711),非常适合车辆结构应用。点焊由刚性梁单元(例如
NASTRAN CBAR)以及以这种形式创建的这些焊缝得到了许多领先的有限元分析专家的支持。
处理器。还支持使用实体元素表示的CWELD和ACM公式,DesignLife会自动识别相关的模型信息,从而实现快速简便的作业设置和解决方案。截面力和弯矩用于计算焊缝边缘周围的结构应力。围绕点焊缝以多个角度增量进行寿命计算,报告的总寿命包括最坏情况。提供的材料数据可应用于许多点焊情况。 Python脚本可以对其他连接方法(例如铆钉或螺栓)进行建模。
4、缝焊
通过“焊缝焊接”选项可以进行包括角焊缝,搭接焊和激光焊在内的焊缝的疲劳分析。该方法基于沃尔沃开发的方法(请参阅SAE文件982311),并已通过多年在车辆底盘和车身开发项目上的使用而得到验证。可以对所有载荷类型(包括振动)进行缝焊分析。应力既可以直接从有限元模型(壳体或实体元素)中获取,也可以根据焊点处的网格点力或位移进行计算。DesignLife提供了可以智能地识别有限元模型中焊缝的方法,从而简化了疲劳工作的设置过程。随软件提供了弯曲和拉伸条件下缝焊的常规材料数据。该方法适用于焊趾,根部和喉咙的故障。
厚焊缝使用ASME锅炉和压力容器规范VI1([2级])标准中概述的应力积分方法进行评估。还可以对板材厚度和平均应力影响进行校正。焊趾处的结构应力,即热点应力,也可以通过在焊缝附近的点外推表面应力来估算。还支持BS7608焊接标准以及所需的材料曲线。
5、一生
在基于CAE的分析软件中首次引入,WholeLife中使用的方法提高了厚焊缝分析的准确性。它使用一种集成方法来对部件从整个早期到最终断裂的整个寿命进行疲劳建模,从而可以更准确地确定焊接寿命,特别是对于复杂的几何形状。 WholeLife使用与缝焊相同的结构应力技术来确定焊缝处的结构弯曲和膜应力。
WholeLife使用厚度方向的应力分布进行几何设计,并且可以包括已知残余应力分布的影响。尽管这主要是基于CAE的分析,但是相同的方法也可以应用于测量的应力数据。
6、胶粘剂
DesignLife使用基于断裂力学的方法来评估结构中最关键的接缝。用梁单元对粘合点进行建模,并使用网格点力确定在粘合法兰边缘处的线力和弯矩。这使得可以在粘合剂的边缘进行近似的应变能释放率(等效J积分)计算,并且通过与裂纹扩展阈值进行比较,还可以计算出安全系数(设计储备系数)
7、振动疲劳
通过“振动疲劳”选项,可以模拟由随机(PSD),扫频正弦波,正弦保压或正弦随机加载驱动的振动台测试。
它提供了在频域中预测疲劳的功能,并且在许多带有随机载荷(例如风和波浪载荷)的应用中,它比时域分析更现实,更有效。求解了有限元模型以进行频率响应或模态分析,并在DesignLife中定义了振动载荷。这可能包括温度,静态偏移负载情况以及组合负载的完整占空比的影响。振动疲劳载荷可用于应变寿命(EN),应力寿命(SN),点焊,缝焊和短纤维复合材料分析。
加速测试是振动疲劳的理想附加产品。它具有根据测量数据创建有代表性的PSD或后扫正弦振动器振动测试的能力。它可以将多个时域或频域数据集组合成具有代表性的测试频谱,从而在不超过实际水平的情况下加快测试速度。
8、热机械疲劳
高温工作环境中的组件(例如发动机活塞,排气系统和歧管)可能会遇到复杂的故障模式。热机械疲劳(TMF)
该选件通过使用有限元模拟的应力和温度结果为高温疲劳和蠕变提供求解器。也可以组合以与温度变化不同的速度变化的机械负载。所需的材料数据来自标准的恒温疲劳和蠕变测试。
TMF包括高温疲劳方法Chaboche和ChabocheTransient。蠕变分析方法包括Larson-Miller和Chaboche蠕变。
9、应变片定位
应变仪定位标志符号可计算最佳位置和所需的应变仪数量,以实现随后的应用载荷历史重构。
荷载重构字形使用单位载荷创建的虚拟应变以及与虚拟应变仪匹配的应变仪测得的应变历史记录来重构导致测得应变的力历史记录。
二、用于复合材料分析的DesignLife产品选项
1、短纤维复合材料
短纤维复合材料选件使用应力寿命方法来分析各向异性材料,例如玻璃纤维填充的热塑性塑料。 从有限元结果中读取整个壳厚度中每个层和截面积分点的应力张量。
通过将制造模拟映射到有限元模型来提供描述每个计算点的“纤维份额”和方向的材料取向张量。 可以从FE结果文件中读取或从ASCI1文件中提供此方向张量。
对于不同的纤维取向,短纤维复合材料分析需要两条或更多条SN曲线的标准材料数据。 DesignLife使用此数据为每个计算点和方向计算合适的SN曲线。 复合材料还支持DesignLife功能,例如多个可变振幅负载和占空比。
2、综合分析
复合分析选项允许用户根据行业标准的复合破坏准则评估结构的强度。 不仅可以将这种评估限于少数情况或步骤,还可以在整个实际工作周期(准静态或动态)中使用选定的失效准则来评估应力。 这样可以很容易地确定关键位置,载荷组合和相关的设计储备系数。 另外,可以在视觉上将所选的位置加载路径与材料破坏包络线进行比较。
可以单独使用以下方法,也可以结合使用以下方法,以得到最保守的结果:
最大压力
●最大应变
●诺里斯
●霍夫曼
●蔡山
●蔡武
●富兰克林·马林
●Hashin
●Hashin-Rotem
●八神
●修改后的NU
●诺里斯·麦金农
●克里斯滕森
●用户定义的自定义
通过Python的方法
3、党范
Dang Van是一种多轴疲劳极限准则,用于预测复杂载荷情况下的耐久极限。 分析的输出表示为安全系数,而不是疲劳寿命。 它使用从拉伸和扭转测试中计算出的特定材料参数。 也可以通过在加载的组件中使用等效塑性应变来说明制造效果。
4、安全要素
安全系数可以计算基于压力的安全系数。 它使用标准的平均应力校正或用户指定的Haigh图来评估耐久性。 该方法被广泛用作发动机和动力总成组件的关键设计标准。
5、处理线程选项
DesignLife可以在具有多个处理器的机器上并行处理。 每个处理线程许可证都允许使用另一个内核。 由于每个模型位置的疲劳计算实际上是独立的,因此添加其他处理线程的好处非常可扩展。 此选项意味着花费更少的时间直接从原始输入转换为最终结果。 通过将翻译分为多个过程,也可以使用多个线程来加快分析的翻译阶段。
6、分布式处理选项
分布式处理使以批处理模式运行的分析可以分布在计算集群的多台计算机或节点上。 它使用高性能计算环境中常见的MPI标准,因此即使最大的有限元模拟也可以高效完成。 这种可伸缩性使您可以通过使用许多计算机的组合处理器来快速解决作业。
ANSYS 2020R1 nCode DesignLife - Release Notes
ANSYS 2020R1 nCode DesignLife provides advanced fatigue analysis integrated within the ANSYS 2020R1 Workbench environment. Results and materials data from simulations within Workbench can be directly accessed by DesignLife. This provides an unparalleled combination of ease of use and powerful fatigue analysis for ANSYS users.
ANSYS 2020R1 nCode DesignLife
Sigma Clipping
Sigma clipping has been implemented for Vibration analyses by a method of controlling the RMS with a clipping factor.
Solid Seam Weld Auto Location
Solid seam weld locations can now be automatically located on the FE model by selection of element groups representing the welds.
Sine-on-Random vibration fatigue enhancement for broadband processes
A new property has been added to the Vibration Load Provider – SineOnRandomCycleCountMethod. This allows the user to specify a Broadband option which considers the bandwidth of the random part in order to reduce the level of conservatism.
DesignLife – Enhancements
Time Step information in CAE Fatigue glyph metadata
Previously, if a DesignLife analysis used a Time Step Load Provider, any Post-Processor Pipe objects with SavePropsToMetadata = True (such as the "Full results" output of many DesignLife glyphs) used metadata to report the load case assigned to each Time Step. This metadata now also includes the steps' time values andscale factors.
Transparency option for status results in the FE Display glyph
The results of a CAE Fatigue analysis often include entities with special statuses rather than actual values, such as No Data or Beyond Cutoff. Entities with a particular status can now be made transparent in the FE Display glyph, so that areas with meaningful results can be found more easily.
TS To FE Table Glyph Enhancements
2 new properties have been added to the glyph. The LoadType property allows the user to set the load type qualifier written to ANSYS XML format files. The ChannelOffset property gives the option for the user to apply a numerical offset to the table ID numbers written in Nastran and Abaqus output files.
FEReader Glyph FRF LoadCase Selection
The FEReader Glyph has been enhanced to simplify the selection of results from FRF vibration results files.
CAE Fatigue glyph warning message limit
The number of warning messages recorded by a logger from a single run of a DesignLife job is now limited. After this limit is reached, only error messages will be logged. This limit may be configured by using the logger's MessageLimit property. Output to the CAE Fatigue glyph's message window is similarly controlled by the glyph's LogMessageLimit property.
Critical Plane normal stress scaling
CAE Fatigue analysis using an SN analysis engine with CombinationMethod = CriticalPlane now has an option ScaleNormalStress. If this is set True, all critical plane normal stresses will be scaled by a factor that represents the influence of shear stress. This option can only be used with SN materials for which the new property FatigueLimitRatio (between shear and tensile fatigue endurance limits) has been defined.
Morrow Mean Stress correction with EN R-Ratio materials
Morrow mean stress correction is now supported in EN analysis for EN R-ratio materials with the restriction that selected materials must contain a single curve with an r-ratio of -1.
Gray iron plasticity calculation improvements
Improvements in the use of the second derivative in the Gray Iron plasticity calculations. This improves the accuracy in some edge cases where the slope of the curve is flat.
Exclusion of results locations connected to rigid element types
A new property has been added which causes entities to be excluded from the analysis when they are attached to certain ‘rigid’ element types.
Exclude support for Material and Property Groups
The GroupNames property now allows the user to specify groups to be excluded. For example setting SelectionGroupType to Property and GroupNames to -SHELL_1,-SHELL_2 will result in all elements in all property groups with the exception of SHELL_1 and SHELL_2 being analysed.
Export of force/moment data from Virtual Sensors
The Virtual Sensor analysis engine can now be used with force/moment data, as well as with displacements. The type of data output is selected using the FE Import Analysis Group's EntityDataType property.
Mounting Virtual Sensor on either Side of a Shell Model
A new ‘Shell Elements’ section has been added to the Virtual Sensor interface that allows a user to mount a Virtual Sensor on the top or bottom surface of a Shell element.
GlyphWorks
GlyphWorks - Enhancements
Workspace Navigation
Navigation of complex flows is now simpler. By double clicking on a glyph entry in the ‘Execution’ tab of the ‘Diagnostics’ window the user may navigate directly to the nominated glyph which will be made visible (and centred if possible) in the currently active view.
Action taken upon Multiple Run Failure
A new boolean preference '/Libraries

lib/StopProcessOnFirstError has been added that controls whether a failure of one of the runs in a multiple run scenario will cause the entire multiple run to abort or to continue and simply announce the error.
Default version of Python switched to 3.6
The default version of Python in nCode 2020 has been switched from Python 2.7 to Python 3.6.
Python 3.6 Text Encoding
The Python 3.6 support has been improved to ensure text encoding is managed correctly and works with extended character sets.
Metadata Calculator Ignore Missing Metadata Option
The new Metadata Calculator glyph MissingMetadata property allows the user to switch between generating an error when an equation references missing metadata items or ignoring that equation and continuing to process any equations which follow.
XY Display move channels between overlays
The XY Display now allows channels to be dragged directly from one overlay to another on the Overlay property page.
Microsoft Excel Multi Column Export
The multi-column output glyph has been enhanced to add the Microsoft Excel worksheet (xlsx) format.
Excel Input Glyph – Process up to first empty column
The Excel input glyph has been enhanced with 3 new properties, MultiColumnAllColumns, ChannelMetaDataAllColumns and TestMetaDataAllColumns. These 3 new properties allow the user to specify a starting cell and the glyph will import multi-column or meta data until it encounters an empty column. This operates in the same way as the 3 AllRows properties of a similar name.
Multi Column Manipulation Glyph – Combine Columns
A new method has been added to the multi column manipulation glyph called CombineColumns. This allows the user to combine columns from 2 separate multi-column objects into a single multi-column object.
Morrow Mean Stress correction in StrainLife with EN R-Ratio materials
Morrow mean stress correction is now supported in the StrainLife glyph for EN R-ratio materials with the restriction that selected materials must contain a single curve with an r-ratio of -1.
New Colour Scheme For Displays
The “mastercol.sys” file has been updated to subtly change the colours used by various displays - an example would be the data lines plotted by the XY Display. The colours used by previous versions of nCode can be restored, if required, by changing a preference.
New preference for default workspace background colour
A new preference has been added to set the default workspace background colour to either white or light grey.
Table Display Colour-coded Cells in Studio
New properties in the Table Display in Studio allow cells to have their background colours set according to threshold levels and to highlight the min/max data values.
GlyphWorks data pipes use colour to show data type
The data pipes in a GlyphWorks flow now use the appropriate colour to show the type of data that they contain (e.g. time series or histogram data). A preference exists to switch back to gray pipes if this is preferred.
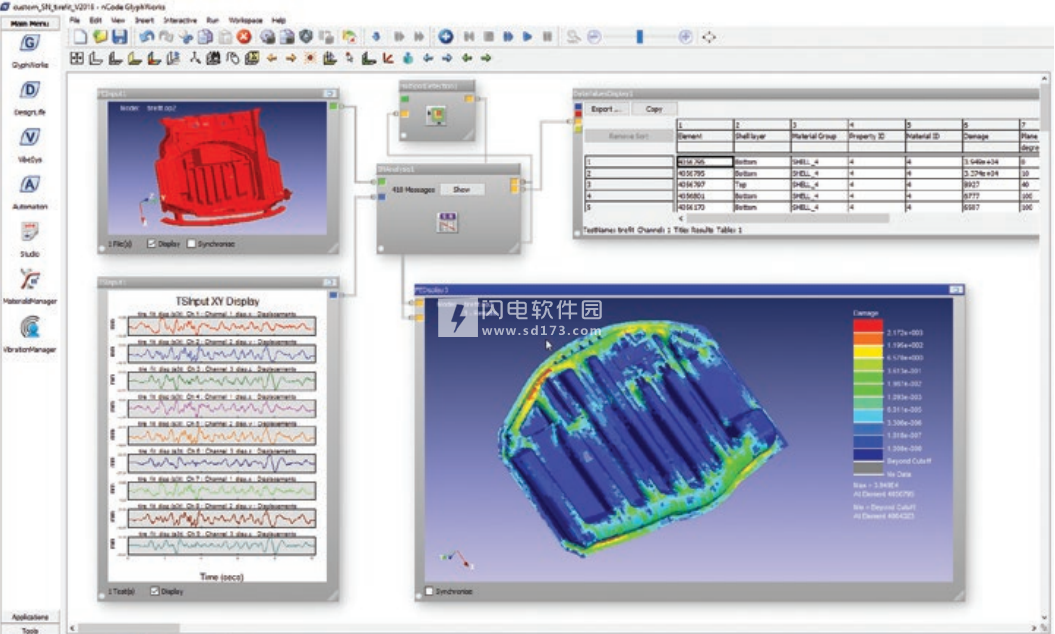
 基于CAE的疲劳分析软件 ANSYS 2020 R2 nCode DesignLife 64位破解版
基于CAE的疲劳分析软件 ANSYS 2020 R2 nCode DesignLife 64位破解版
 基于CAE的疲劳分析软件 ANSYS 2020 R2 nCode DesignLife 64位破解版
基于CAE的疲劳分析软件 ANSYS 2020 R2 nCode DesignLife 64位破解版
 lib/StopProcessOnFirstError has been added that controls whether a failure of one of the runs in a multiple run scenario will cause the entire multiple run to abort or to continue and simply announce the error.
lib/StopProcessOnFirstError has been added that controls whether a failure of one of the runs in a multiple run scenario will cause the entire multiple run to abort or to continue and simply announce the error.